A brief review of Aloha Airlines and Flight 243
Aloha Airlines Flight 243, which operated on a regular schedule between Hilo and Honolulu in Hawaii, faced a significant incident on April 28, 1988. During the flight, an unexpected explosive decompression occurred due to a section of the aircraft’s body failing. This incident was a result of both inadequate maintenance procedures and metal fatigue. The subsequent investigation revealed the crucial role these factors played in the event.
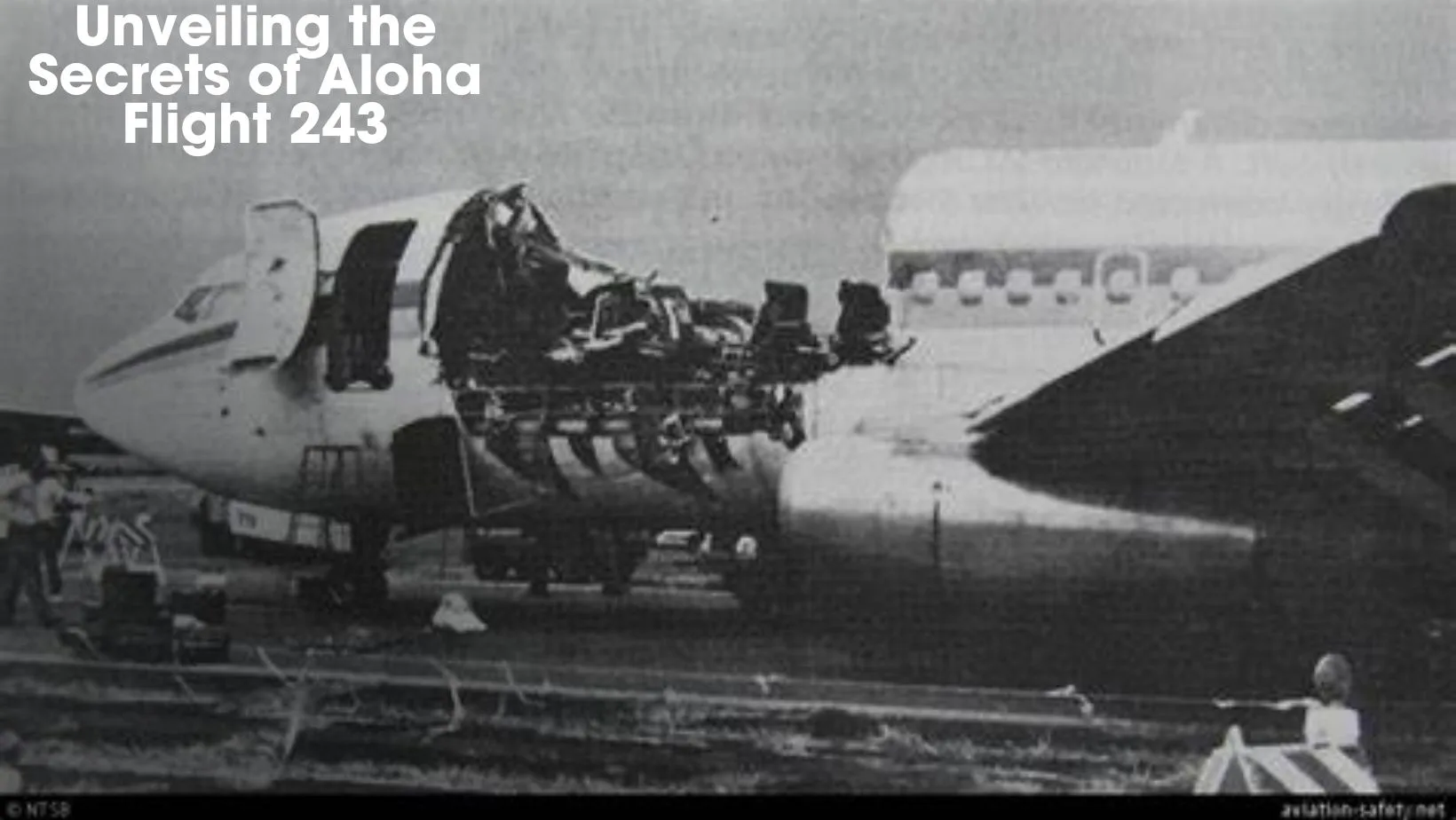
The structural damage to the Boeing 737-297 aircraft was extensive, creating a dangerous situation for both the crew and passengers on board. This incident underscored the vital importance of proper maintenance procedures and raised awareness about the potential risks associated with metal fatigue in aircraft structures.
History and services of Aloha Airlines
Aloha Airlines, initially founded as Trans-Pacific Airlines in 1946, aimed to compete with Hawaiian Airlines. Starting with just one aircraft, the airline quickly gained popularity and earned the nickname “The Aloha Airline.” It officially became Aloha Airlines in 1958.
Over the years, the airline encountered various challenges, including tough competition in the market, rising operational costs, and external events such as the 9/11 attacks and increases in fuel prices. These difficulties led to financial struggles, prompting Aloha Airlines to file for bankruptcy protection twice—first in 2004 and again in 2008. Despite their efforts to overcome these challenges, the airline had to suspend all passenger flights in March 2008, resulting in employee layoffs.
To cope with the situation, the company decided to sell its successful freight and contract services division to Saltchuk Resources, an established player in the Hawaiian market. This strategic move was made to salvage some part of the business amidst the challenging circumstances.
Event Information: Day, Time, and Area
On April 28, 1988, at 1:25 PM, Aloha Airlines Flight 243 experienced a catastrophic event at Hilo International Airport terminal. The aircraft had already completed three uneventful round-trip flights earlier that day. Before departure, the pre-flight inspection didn’t reveal any abnormalities, and there were no weather advisories for the intended route.
The flight proceeded normally until around 1:48 PM when the airplane was about 23 nautical miles south-southeast of Kahului, Maui. It was at this moment that a section on the left side of the airplane’s roof ruptured with a distinctive “whooshing” sound. The aircraft’s captain felt a sudden jolt and encountered instability, while the first officer observed airborne pieces of grey insulation within the cockpit. The cockpit door broke away, revealing an open view where the upper ceiling had once been.
The extent of the damage was substantial; a large portion of the roof, approximately 18 feet in diameter, had torn off from behind the cabin to the fore-wing area. These events occurred during the flight at an altitude of 24,000 feet (7,300 m), disrupting the normal operation of the aircraft and creating a dangerous situation for everyone on board.
Description of the airplane
It was the Boeing 737-200, which was the 152nd aircraft produced at the Renton assembly Unit. It was delivered in 1969 to Aloha Airlines brand new having registration number N73711. Over its service life, the aircraft had accumulated 35,496 flight hours and nearly 90,000 flight cycles, exceeding the intended design limitations.
The Sequence of Occasions and Causes
At precisely 1:25 p.m. on a typical Thursday, Aloha Airlines Flight 243 commenced its journey from Hilo to Honolulu. Initially, passengers settled into their seats, engrossed in various activities like reading, working, or simply trying to unwind.
Unbeknownst to the pilots, a sudden and significant change in pressure occurred. This caused the aircraft’s floor to rise, breaking numerous floor beams and damaging the cable connected to the left engine. Consequently, the plane started shaking violently, posing a challenging situation for the pilots, Schornstheimer and Tompkins.
Schornstheimer promptly took control of the plane, focusing on stabilizing it and initiating an emergency descent toward Maui. Realizing the extensive damage, he decided against attempting to restore the cabin’s pressure, understanding it would be futile and potentially perilous. Managing the aircraft became even more challenging as it was now flying faster than usual, at around 170 knots, or just over 195 mph. Previous attempts to slow down the plane had only exacerbated the violent shaking.
Finally, at 1:58 p.m., the aircraft landed tensely on the runway of Kahului Airport, with the front landing gear lowered. However, the danger was not yet over. As aircraft rescue firefighters hurried to the scene, a makeshift area was swiftly established near the plane to provide immediate medical care to any passengers or crew members who might have been injured.
Rescue and Emergency Actions
Following the emergency situation involving the plane at Maui Airport terminal, the fire department responded promptly, dispatching five emergency vehicles to assist. Passengers who were able to walk left the aircraft using slides and the back airstair. Once the area was secure, fire department personnel entered the plane to aid the injured passengers still aboard. Remarkably, within 25 minutes, all passengers were successfully evacuated from the plane.
Initially, the flight crew informed the air traffic control service (ATC) about a “rapid decompression” situation but didn’t provide specific details about the extent of the structural damage. The ATC promptly alerted the rescue and firefighting teams, although they didn’t immediately request ambulance assistance. Later, at 13:53, the flight crew confirmed their need for passenger assistance upon landing, which was acknowledged by the ATC. According to police dispatcher records, the “Medic I” ambulance was alerted at 13:58, around the same time the aircraft touched down. The reason for notifying the ambulance late remains unknown. The first rescue team arrived at the scene at 14:05 and called for additional assistance.
Investigation and Contributing Factors
NTSB (National Transportation Security Board)
The NTSB performed the investigation and released a report outlining their findings. According to the report, the accident was most likely caused by a failure in Aloha Airlines’ maintenance program, by the operator of the airplane. The maintenance program failed to identify significant fatigue and dis-bonding damages on the aircraft, particularly in the body. These damages end up in the separation of the upper portion of the fuselage.
The management of Flight 243 also shared responsibility for the crash. They failed to adequately supervise the maintenance employees working for the airline, which could have helped identify and address the issues with the aircraft before the accident occurred.
FAA (Federal Aviation Administration)
Following the tragic crash of Aloha Airlines Flight 243, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) played a pivotal role in investigating the incident and instigating vital changes in aircraft inspection and maintenance protocols. The accident highlighted various factors that contributed to the disaster, including shortcomings in FAA regulations, flaws in the design and manufacturing of the Boeing 737 aircraft, and subpar maintenance practices by the airline.
FAA Oversight and Inspection Reforms
Following the Aloha Airlines Flight 243 incident, the FAA initiated comprehensive reforms in aircraft inspection and maintenance procedures. Recognizing the critical importance of regular and rigorous inspections, the FAA introduced stringent evaluation programs for aging aircraft. These programs focused on meticulous examinations of crucial components, ensuring that potential issues were identified and addressed before they could compromise flight safety.
One of the key changes involved the revision of FAA regulations, specifically in the form of the review of Regulation 25.571. These revisions encompassed both older airplanes and newly certified aircraft, establishing retroactive requirements that mandated thorough inspections for structural integrity. These measures were put in place to guarantee the continued safety of older planes while also ensuring that new aircraft entering service adhered to stringent safety standards.
Human Element and Certification Emphasis
In response to the accident, the FAA emphasized the paramount importance of the human element in aircraft maintenance and inspection. This recognition led to the implementation of certification programs for maintenance personnel and supervisors. These certifications mandated comprehensive training in repair procedures, ensuring that maintenance workers were equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to identify and rectify structural issues effectively.
Additionally, inspectors and technicians were required to obtain unquestionable qualifications, reinforcing the expertise needed to evaluate aircraft integrity thoroughly. By focusing on human resources, the FAA aimed to bolster the competence of the workforce responsible for ensuring the safety and airworthiness of commercial aircraft.
Conclusion: Enhancing Air Safety Through Comprehensive Reforms
In conclusion, the Aloha Airlines Flight 243 crash spurred transformative changes in the aviation industry. The proactive approach of the FAA in addressing regulatory gaps and emphasizing the human element in aircraft maintenance has significantly improved air safety standards. Through rigorous inspections, comprehensive training, and unwavering commitment to certification, the FAA has played a pivotal role in fostering a culture of safety. This ensures that similar incidents are prevented, instilling confidence in passengers regarding the stringent safety measures governing air travel.
Following the crash, survivors and the families of the victims chose to pursue legal action against both Aloha Airlines and the aircraft manufacturer. These lawsuits aimed to seek compensation for the physical and emotional damage caused by the tragic event.
Summary of Injuries
The crash of Aloha Airlines Flight 243 had profound and enduring psychological effects on both the passengers and the crew members who were onboard. Many individuals struggled significantly in recovering from the traumatic experience and were diagnosed with post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Overcoming the emotional trauma posed considerable challenges for them.
Lesson from Aloha Airline 243
The survival of Aloha Airlines Flight 243, despite experiencing a fuselage rupture over Hawaii, served as a stark wake-up call for the air transport industry. Despite only one fatality, the crash exposed deep-rooted issues and underscored the dangers of complacency. The investigation revealed that the factors leading to the crash were well-known but had been disregarded. The incident highlighted the urgent need for significant improvements in airline practices and regulatory oversight.
The industry had grown complacent about maintenance and the durability of aging aircraft, ignoring well-known vulnerabilities in the body design. The accident prompted a reevaluation of inspection procedures, the implementation of mandatory corrosion control programs, and a focus on proper repairs and maintenance. The crucial lesson learned was that safety should never be taken for granted; continuous effort and vigilance are necessary to uphold the industry’s safety record.






Leave a Reply