The Risk-Based Approach (RBA) in aviation is a systematic strategy for prioritizing safety and security by identifying, assessing, and mitigating aviation-related hazards. This strategy has gained popularity as aviation systems become more complex, necessitating smart resource allocation to improve safety and security. Since the event of 9/11, there have been many attempts to breach aircraft security in flight. These range from shoe bombs to dirty bombs, explosives, liquids, aerosols, or gels. In every situation, the global aviation community has taken pre-emptive and preventive measures. New emerging threats to civil aviation are a critical challenge to the aviation safety and security system but the international civil organization is addressing and making proactive measures regarding these threats and they will continue to do so on a global basis.
Risk Assessment Process
A risk assessment is about identifying sensible measures to control the risks in your workplace.
- Identify the hazard
- Identify the people who are at risk
- Evaluate the risk and decide on the precautions
- Decide on control measures to implement
- Document the findings
Hierarchy of control to deal with risk:
- Elimination
- Substitution
- Engineering controls
- Administrative controls
- PPE(personal protective equipment)
The first step in controlling the risk is simply to remove the hazard from that area and this is the most effective way. Further, if we can’t eliminate the hazard we can substitute that hazard (replacing the hazard). After that, we can further control by isolating people from the hazard. Then change the way the people work (administrative control). At last the least effective is giving people personal protective equipment for their safety.
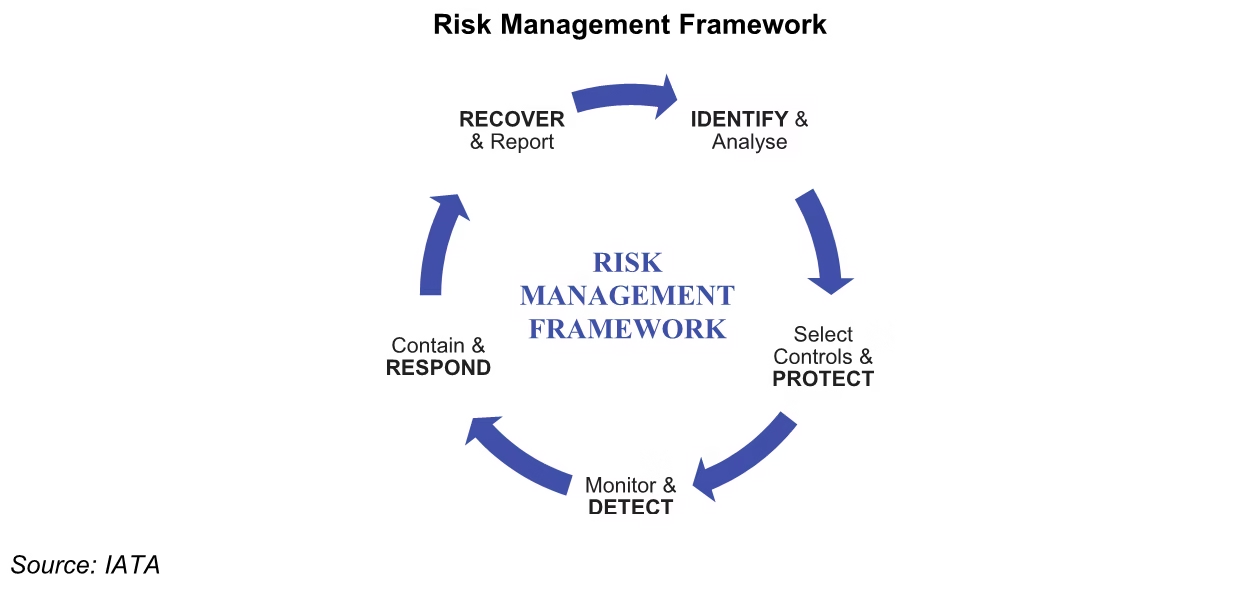
Risk Management Process
Risk is equal to probability*severity. Probability is the number of times you are exposed to risk and severity is the level of damage it can cause. We can also say that probability is equal to exposure and severity is equal to outcomes. The bad outcomes from the risk exposure. E.g., cut by a knife, accident due to overspeed, fall injury, shock by electricity, etc. The goal of risk management is to proactively identify safety-related hazards and mitigate the associated risks.
Risk management process
- Identify hazards
- Assess risks
- Analyze control
- Make control decisions
- Use control
- Monitor results
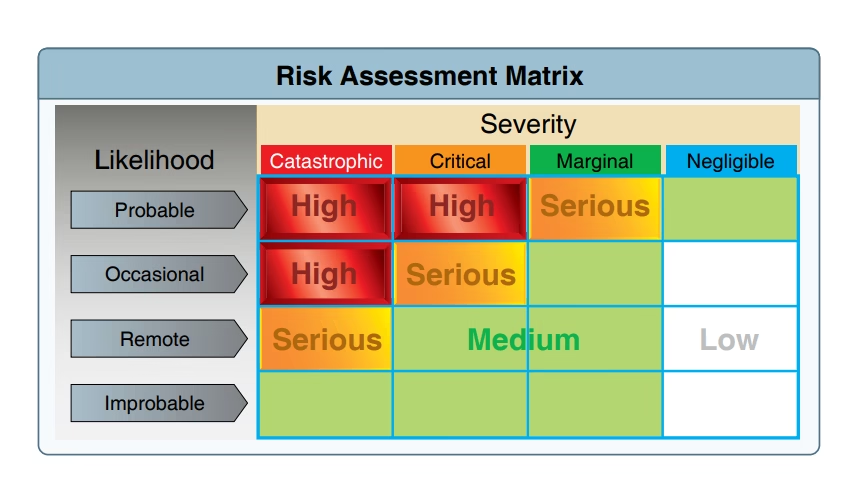
Risk Assessment Matrix
Safety/security risk is the assessment of hazard from probability and severity known as the risk assessment matrix. The risk assessment matrix is the table by which we can qualitatively and quantitatively find the risk. In this matrix, we take likelihood at the y-axis and severity at the x-axis. The likelihood is the probability of occurrence and severity is the damage or injury the hazard have. For example: a Hazard is an earthquake so, its severity is critical and likelihood is occasional then by risk assessment matrix says that the risk is serious.
For hazards, proper risk management techniques should be implemented in the system. The goal of risk management is to proactively identify safety-related hazards and mitigate the associated risks. The risk management process involves the following steps:
- Identify hazards
- Assess risks
- Analyze control
- Make control decisions
- Use control
- Monitor result
Risk Management Handbook (FAA-H-8083-2A) | Federal Aviation Administration
FAA Handbook






Leave a Reply